Publié sur :
Publication Powerpoint Delepine - 2003
Voir la version PDF de cette publication :

Periosteal Ewing's sarcoma Report of six cases
F. Delepine, G. Delepine, H. Cornille,
Nicole Delepine
Periosteal Ewing's sarcoma Report of six cases
Introduction
Few cases of periosteal Ewing's sarcoma have been reported and the surgical implications of such a diagnosis have not been underlined.
The aim of this study is to evaluate the actual incidence
The consequence for surgical treatment.
Material
Our file of 148 patients treated for ewing's sarcoma of bone throughout 1982-2002 have been examined to see if they fit the diagnostic criteria and to evaluate the pronostic value and the therapeutic implications of it.
Definition of periostal Ewing's sarcoma
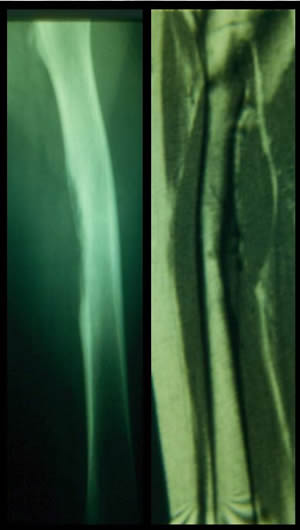
The reported cases fulfilled the diagnosis criteria defined by Bator :
- Ewing's sarcoma of bone histologically confirmed with a pure periosteal location without medullary extension.
Results
Out of 148 Ewing's sarcomas of bone of our file, only six (4 %) could be classified as PES.
All involved the femur in the diaphyseal (2) or metaphysodiaphyseal (4) locations.
According to Ennecking classification 2 tumors were graded II A and the 4 other II B.
Age of the patients ranged 11 to 19.
All patients were treated by resection after preoperative chemotherapy.
One was irradiated.
Case 1
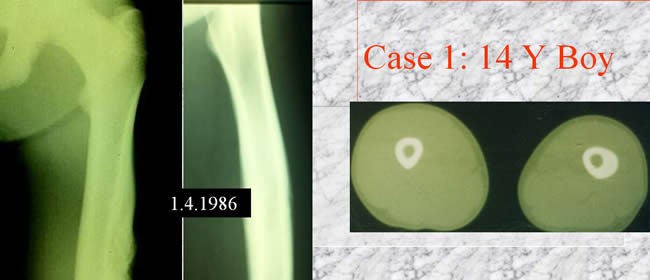
CT scan showing diaphyseal thickening no medullary involvment no soft tissue extension.
Case 2
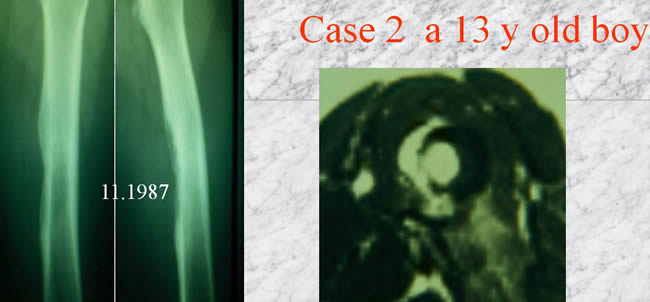
NMR showing a hemidiaphyseal tumor
CT scan without medullary invasion
Case 3
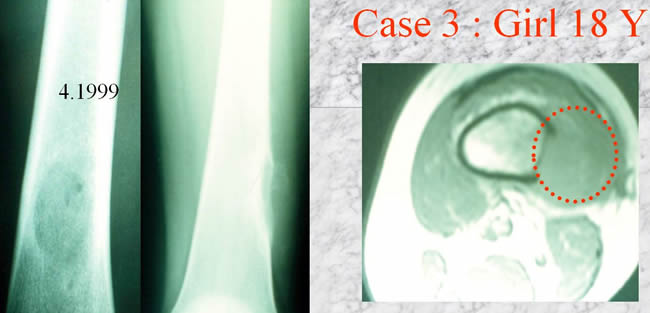
- NMR showing a soft tissue mass
- a remaining endocortical line
- no medullar tumor
Case 4
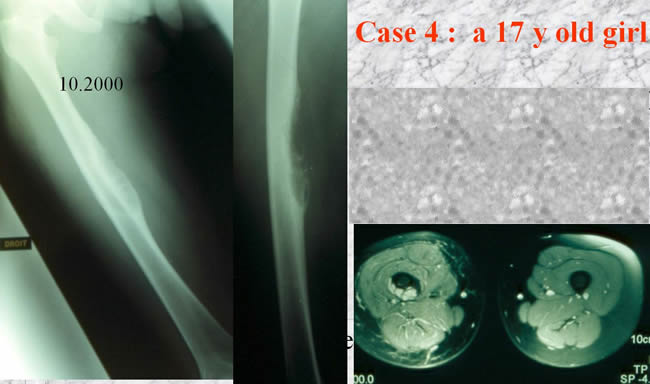
- NMR showing a small soft tissue mass
- no medullary tumor
Case 5
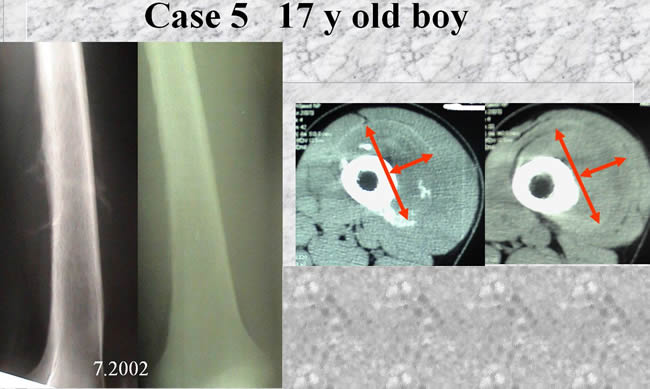
- NMR showing a soft tissue mass
- no medullary tumor
Case 6
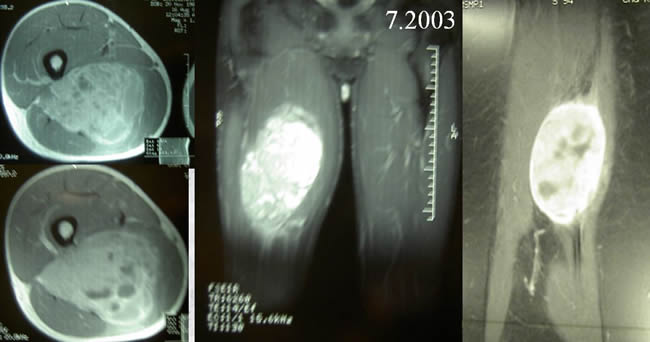
- NMR showing a big soft tissue mass (10-8 cms)
- no medullary involvment
The two first patients were not recognized as PES : case 1
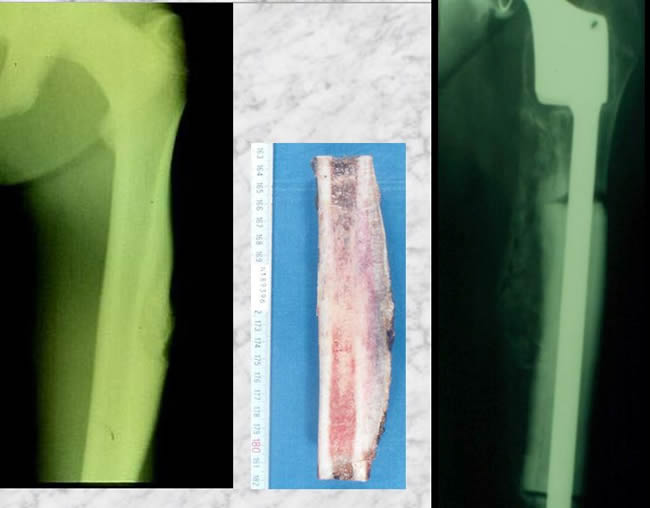
They were treated by wide resection interrupting the femoral continuity and skeletal reconstruction using massive prostheses.
The two first patients were not recognized as PES case 2
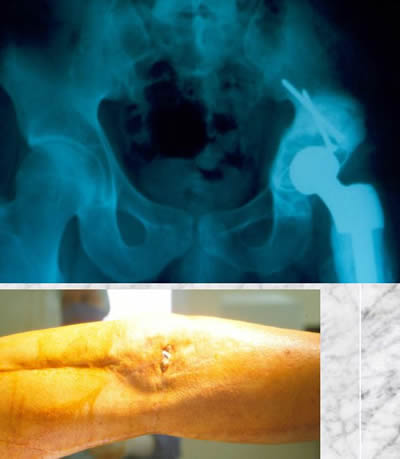
Both have still their prostheses but the orthopaedic evolution of both was complicated compelling to reoperate.
One of the patients suffered of acetabular wear and loosening (3R).
The second suffered of deep infection (6R).
The four other patients were diagnosed as PES before the biopsy case 3
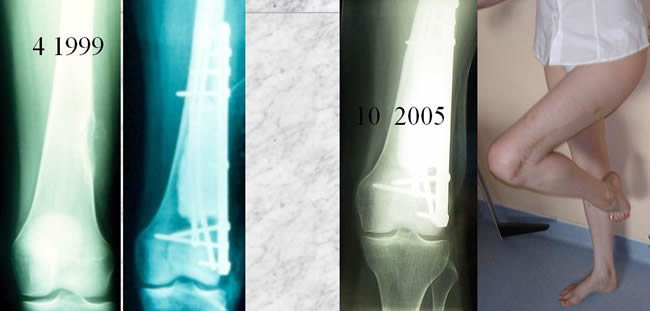
Partial bone resection with definitive acrylic cementation.
- 6y follow up
- no reoperation
- excellent function
In case 4 the extension compelled us to interrupt the continuity of the diaphysis
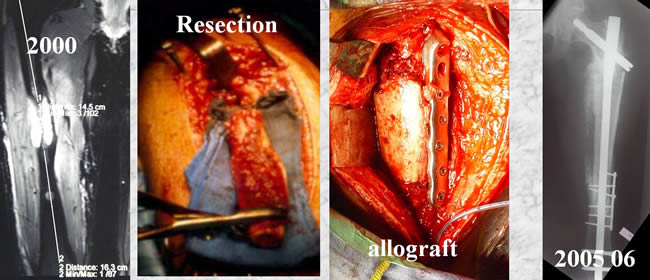
Three reoperations were necessary to achieve bone healing.
The four other patients were diagnosed as PES before the biopsy Case 5
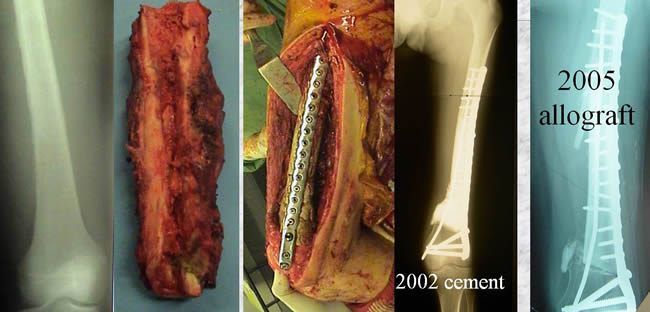
Cementation during chemotherapy.
Definitive reconstruction with allograft.
Excellent result.
The four other patients were diagnosed as PES before the biopsy Case 6
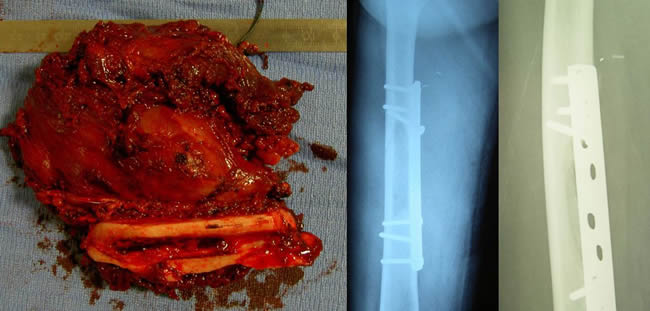
Wide resection plating.
Excellent result.
Oncologic results
With an average follow up of 9 years all 6 patients are even free survivors.
Comments
The prognosis of PES looks better than that of common Ewing's sarcoma even in case of big tumoral volume like cases 3, 5 and 6.
In the literature 28/30 (94%) patients with PES were DFS at last consultation the better prognosis of PES should prevent inclusion of patients in too heavy chemotherapy protocols.
surgical implications of periosteal location must be underlined : biopsy

When the diagnosis is pre biopsy suspected on CT and MRI, the biopsy should be confined to the cortical bone or the soft tissues without cortical perforation and medullar contamination.
The preferred treatment is partial resection without interruption of the bone continuity
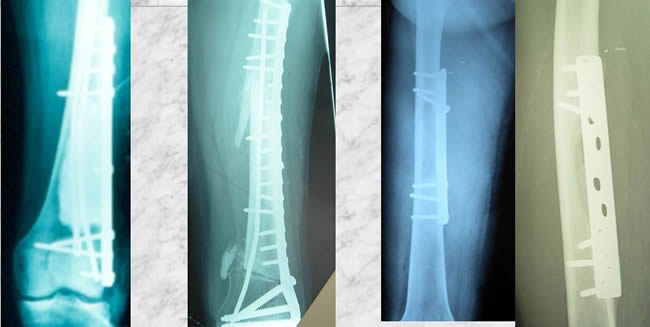
Such a procedure permits much easier reconstruction without massive material.


